
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/network-computer-special-ip-address-818385-A-v1-5b44f12346e0fb0037c10c4a.png)
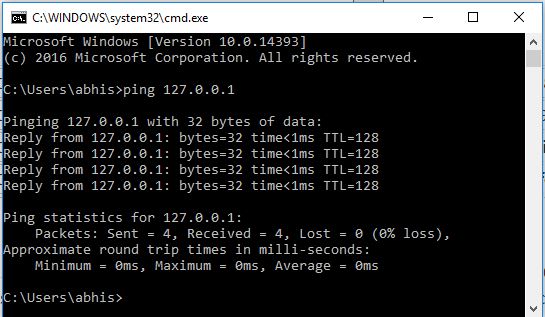
Please check below ping results to 127.0.0.0 and 127.255.255.255, which shows "General failure" in Windows TCP/IP implementation. Network address and directed broadcast address of loopback address range are not reachable. Though it is the most common and most famous, 127.0.0.1 is just one address out of a large block, 127.0.0.0 127.255.255.255, that is reserved for loopback purposes in RFC 6890. The random IPv4 loopback address selected is 127.10.100.50. Both screen shots show that ping command got reply from loopback addresses.īelow screenshot shows ping reply from localhost IPv4 loopback address, 127.0.0.1.īelow screenshot shows ping reply from a random IPv4 loopback address from 127.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 network.

For example below two screen shots show the output of ping command (from a Windows machine) from two IPv4 loopback addresses. The solution is IPv6, and no amount of reclaiming IPv4 addresses is going to solve the situation. There are only about 4 billion possible IPv4 addresses, but there are well over 5 billion devices on the Internet, and it is growing every day.
Other IPv4 addresses in 127.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 network (from 127.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.254) are also up and reachable. 2 That number of IPv4 addresses is barely a drop in the bucket. Its mainly for troubleshooting of the NIC and can be mixed up to different IP addresses using class A IP. Loopback address is 127.0.0.1 is mapped to hostname localhost internally. Like our physical interface, we assign a special IP address which is called a loopback address or loopback IP address. The loopback subnet is not routable on the internet. The most widely used IPv4 loopback address is 127.0.0.1. Any data traffic sent to IPv4 loopback addresses from 127.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.254 as the destination IPv4 address will never appear on network. In other words, if you ping to a loopback address, you get the reply from the TCP/IP protocol stack running on the same computer. When any program/protocol sends data from a computer with any IPv4 loopback address as the destination address, the TCP/IP protocol stack on that computer process the traffic within itself without sending it to the network.

Hence you can use the loopback IP addresses for TCP/IP troubleshooting purposes. The loopback IP addresses are always available. Loopback addresses mock TCP/IP Client/Server on the same machine. Loopback IP addresses are managed by the TCP/IP protocol suite within the operating system. As mentioned in previous lessons, 127.0.0.0 is the network address and 127.255.255.255 is the directed broadcast address for 127.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 network. The most common IPv4 address used is 127.0.0.1. Various Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standards reserve the IPv4 address block 127.0.0.0/8, in CIDR notation and the IPv6 address ::1/128 for this purpose. The loopback network in IPv4 is 127.0.0.0 with a subnet mask of 255.0.0.0. Unix-like systems usually name this loopback interface lo or lo0. An entire Class A network itself is reserved as loopback network. Datacenter Proxies 80M+ datacenter proxies that provide quick internet access at reasonable costs Email Marketing Infrastructure Infrastructure Dedicated Servers Bare metal servers that meets your business needs. 127.0.0.1 is the address most commonly used for testing purposes.IPv4 has special reserved addresses called as loopback addresses. Since the lower layers are short-circuited, sending to a loopback address allows the higher layers (IP and above) to be effectively tested without the chance of problems at the lower layers manifesting themselves. The purpose of the loopback range is testing of the TCP/IP protocol implementation on a host. Instead, they “loop back” to the source device. The data sent by a host to a 127.x.x.x loopback address are not passed down to the data link layer for transmission. Looback address is a special range of addresses in the range 127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255. Within IPV6 loopback looks like 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, although in IPV6, the longest contiguous block of zeros may be replaced with :: thus resulting in the condensed loopback address of ::1, based upon RFC 4291: IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture. To configure the primary loopback interface IP address: Select Network > Loopback. The loopback interface has no hardware associated with it, and it is not physically connected to a network. A loopback interface is also known as a virtual IP, which does.
#Loopback ipv4 address software#
Is a special IP number (eg: 127.0.0.1) that is designated for the software loopback interface of a machine. The IPv4 designated 127.0.0.1 as the loopback address with the 255.0.0.0 subnet mask. Loopback address, based upon RFC 5735: Special Use IPv4 Addresses, Loopback address is a special IP number (127.0.0.1) that is designated for the software loopback interface of a machine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
